

Fountain Valley Urgent Care Permanently Closed. We’re Here to Care for You at Our Other Locations.
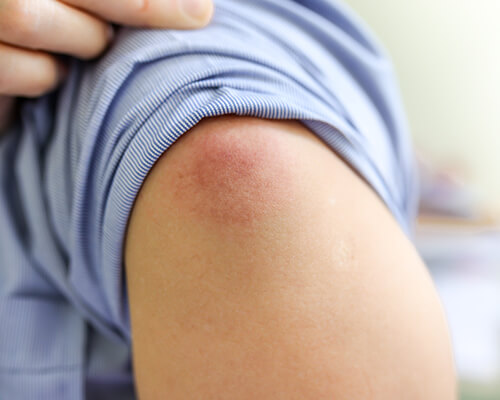
Cuts or breaks in the skin allowing bacteria to enter causes cellulitis, an infection of the skin and underlying tissue. While it’s a common infection, it can spread and cause severe health complications if not properly treated. At our urgent care centers in Orange County, CA, we can treat cellulitis on the hands, face, eyes, feet, arms, and anywhere else on the body with our personalized treatment and care. Our offices are located in Irvine, and Costa Mesa.
Highlights of Our Urgent Care Centers:
With the onset of the condition, it is quite common to experience pain and tenderness, skin swelling, redness or red strikes, and blisters on the infection site. You can also experience warm skin, fever, chills, headaches, fatigue, and bruising.
Leaving these symptoms untreated can quickly spread the infection and cause severe symptoms, such as:
Seek immediate medical care if you are a diabetic or have a weakened immune system and experience any of these symptoms of cellulitis.
We may perform these procedures for diagnosing cellulitis:
With on-site lab and X-ray facilities, we can quickly deliver test results to help begin your treatment as soon as possible.
Depending on your test results, age, the severity of your infection, and overall health condition, we will tailor an appropriate treatment plan that may include:
Untreated cellulitis may cause complications like:
Septicemia
It occurs when the infection spreads to your bloodstream, causing persistent fatigue and chronic pain. Amputation may be required even when the condition is not fatal.
Gangrene (Tissue Death)
Lack of blood supply to the tissues causes gangrene. If not treated in time, it may require amputation, and become life-threatening.
Abscess
An abscess is a pocket of pus that develops under the infected skin or between skin layers. Surgery might be required to treat it.
Necrotizing Fasciitis (Flesh-Eating Disease)
It is an infection of the deepest layer of skin that can spread to your fascia or the connective tissue surrounding your muscles and organs, causing tissue death.
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA)
MRSA, a severe staph bacterium, can also cause cellulitis. It is resistant to antibiotics used to treat normal staph infections.
Cellulitis does not appear severe in the beginning. However, if left untreated, the infection can spread to your bloodstream and lymph nodes, resulting in a life-threatening condition. So, if you are experiencing cellulitis symptoms or suspect having this infection, walk into one of our urgent care clinics. We provide comprehensive medical care to diagnose and treat cellulitis so you can get back to your regular activities.
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that affects the deeper layers of the skin and underlying tissues. Symptoms include redness, swelling, warmth, pain or tenderness in the affected area, fever, and in some cases, blisters. The infection often occurs in the legs, arms, or face.
Cellulitis is typically diagnosed at urgent care through a physical examination, where the healthcare provider looks for signs of redness, swelling, and warmth. In some cases, blood tests or cultures may be taken to identify the bacteria causing the infection.
Cellulitis is most often caused by bacteria, such as Streptococcus or Staphylococcus, which enter the skin through cuts, scrapes, insect bites, or other breaches in the skin. It can also occur after surgery or from conditions like athlete’s foot, which can lead to skin breakdown and increase the risk of infection.
Treatment for cellulitis at urgent care typically includes antibiotics, which may be oral or intravenous (IV), depending on the severity of the infection. Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications may also be prescribed. In some cases, if an abscess is present, drainage of the infection may be necessary.
Cellulitis typically requires prescription antibiotics, and over-the-counter medications are not sufficient to treat the infection. However, over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can be used to manage pain and reduce inflammation until you can see a healthcare provider.
With proper treatment, most cases of cellulitis improve within 3 to 7 days. However, it may take several weeks for the skin to fully heal and for redness and swelling to subside. If the infection does not improve or worsens, follow-up care is necessary.
If you suspect you have cellulitis, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Early treatment with antibiotics can prevent the infection from spreading or becoming more severe. If you notice increased redness, swelling, pain, or fever, go to urgent care or your healthcare provider for an evaluation.
Yes, if left untreated, cellulitis can spread to other parts of the body, including the bloodstream, potentially leading to a more serious infection like sepsis. The infection can also affect deeper tissues and organs. Prompt treatment with antibiotics is necessary to prevent complications.
Complications from untreated cellulitis can include abscess formation, sepsis (a life-threatening infection that spreads throughout the body), and tissue death (necrosis). In severe cases, untreated cellulitis can lead to amputation or permanent scarring.
Cellulitis itself is not contagious, but the bacteria that cause it can be spread through direct contact with an infected wound or skin. To prevent the spread of bacteria, avoid touching the infected area, and wash your hands thoroughly after caring for the wound or infected area.

We're Open Every Day!
Mon - Fri:
8AM - 8PM
Weekends & Holidays: 8AM - 5PM

We're Open Every Day!
Mon - Fri:
8AM - 8PM
Weekends & Holidays: 8AM - 5PM